Your Patients May Ask You
What is an Ultrasound scan?
 An ultrasound scan is a method of imaging the body using high
frequency sound waves. A hand held probe is placed against the skin, to which, an
ultrasound gel has been applied. This in turn allows the sound waves to travel
into the body. The probe can then be moved across the body to scan and image
various organs and structures. These are then displayed on the system's monitor
for interpretation by an appropriately qualified medical professional.
An ultrasound scan is a method of imaging the body using high
frequency sound waves. A hand held probe is placed against the skin, to which, an
ultrasound gel has been applied. This in turn allows the sound waves to travel
into the body. The probe can then be moved across the body to scan and image
various organs and structures. These are then displayed on the system's monitor
for interpretation by an appropriately qualified medical professional.
What does the equipment look
like?
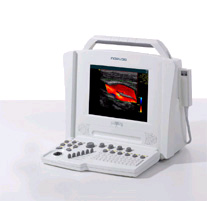
Ultrasound scanners consist of a
console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to scan the body. The transducer is a small hand-held device that
resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. The transducer sends
out a high frequency sound wave and then listens for a returning sound wave or
"echo."
 The ultrasound image is
immediately visible on a nearby screen that looks much like a computer or
television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (strength),
frequency and time it takes for the sound signal to return from the patient to
the transducer.
The ultrasound image is
immediately visible on a nearby screen that looks much like a computer or
television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (strength),
frequency and time it takes for the sound signal to return from the patient to
the transducer.
Is there any special preparation?
Abdominal studies require some
preparation. Upper abdominal scans (limited or complete abdominal, gallbladder,
liver, pancreas, aorta, spleen) require you not to eat for at least six hours
prior to the start of the exam. This enables the gallbladder to fill, keeping
the stomach empty and reducing intestinal gas.
For renal scans, you will need to
have a full bladder. It is best to start drinking 4-5 glasses of water of fluid
an hour before the examination.
Who will I see?
A State-certified, appropriately trained radiologist
or sonographer, depending on what type of examination you are having.
What happens during the scan?
You will be asked about your
health and current symptoms relating to the scan. You will be asked to lie down
on the couch. You will be asked to remove clothes away from the area being
examined.
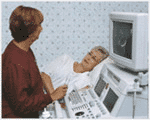
The sonographer will sit or stand
by your side and gel will be applied to the skin. A probe is gently moved across
the area of interest. You may be asked to roll onto your side, sit or even
stand during the examination.
For abdominal examinations you
will be asked to take deep breaths and hold your breath for a few moments.
 Occasionally the bladder may not be full enough to assess and
you will be asked to drink some more fluid and sit and wait until the bladder
fills.
Occasionally the bladder may not be full enough to assess and
you will be asked to drink some more fluid and sit and wait until the bladder
fills.
How long will it take?
Most examinations take 30-45
minutes. More specialized scans can take up to an hour, such as vascular
examinations of blood flow.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and
interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report
to your primary care or referring physician, who will share the results with
you. In some cases the radiologist may discuss preliminary results with you at
the conclusion of your examination.
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- Ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no
needles or injections) and is usually painless.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use
and less expensive than other imaging methods.
- Ultrasound imaging uses no ionizing
radiation.
- Ultrasound scanning gives a clear picture of
soft tissues that do not show up well on x-ray images.
- Ultrasound causes no health problems and may
be repeated as often as is necessary if medically indicated.
- Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality for the diagnosis and monitoring of pregnant women and their unborn
infants.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, making
it a good tool for guiding minimally
invasive procedures such as needle
biopsies and needle
aspiration of fluid in joints or elsewhere.
Risks
Are there any side effects?
No. There are no side effects.
What are the limitations of General Ultrasound Imaging?
Ultrasound waves are reflected by air or gas; therefore
ultrasound is not an ideal imaging technique for the bowel. Barium exams and CT scanning are the methods of choice for bowel-related problems.
Ultrasound waves do not pass through air; therefore an
evaluation of the stomach, small intestine and large intestine may be limited.
Intestinal gas may also prevent visualization of deeper structures such as the
pancreas and aorta. Patients who are obese are more difficult to image because
tissue attenuates (weakens) the sound waves as they pass deeper into the body.
Ultrasound has difficulty penetrating bone and therefore can only see the outer
surface of bony structures and not what lies within. For visualizing internal
structure of bones or certain joints, other imaging modalities such as MRI are typically used.
Can I eat and drink afterwards?
Yes. Follow your normal dietary routine.

Ultrasound Tests Tutorial
 2-D
& M-MODE ECHO
2-D
& M-MODE ECHO
 CARDIAC
DOPPLER
CARDIAC
DOPPLER
 COLOR
FLOW
COLOR
FLOW
- 2-D & M-MODE ECHO – This exam uses sound waves to produce images of
the heart as it is beating. This enables the Cardiologist to evaluate your
valves, size of the heart chambers, and the strength and thickness of your
heart muscle. The complete exam takes
approximately 45 minutes. There are no special preparations or
instructions for this exam.
- DOPPLER – This exam is usually
performed with the echocardiogram. The Doppler uses sound waves, which
reflect off the moving red blood cells within the heart chambers. The
Doppler reveals the speed and direction of blood flow within the heart,
which is helpful in evaluating valve function.
- COLOR FLOW - This is usually done in
conjunction with the Doppler test. It shows the speed and direction of
blood flow in color. The color allows the Cardiologist to "map"
abnormalities in blood flowing through the heart and great vessels.
Cardiac Symptoms: Hypertension, Chest
Pain, Murmur, Syncope, Arrhythmia, Suspected coronary artery disease, Valvular
heart disease, Endocarditis, Pulmonary disease, Cardiac masses, Evaluation of
ventricular function, Stroke, Peripheral emboli involving major arteries, and
Family history of genetic cardiac disorder.
 CAROTID DUPLEX SCAN
CAROTID DUPLEX SCAN
CAROTID – This exam uses
sound waves to visualize the right and left common carotid arteries from the
base of the neck to above the bifurcation of the internal and external carotid
arteries. The vertebral artery (posterior in the neck) is also imaged. The
physician evaluates the images to determine to what extent these arteries are
blocked. Doppler is used to show how much blood is flowing to your brain and eyes. The length of this test is 45 minutes. No preparation is needed.
Symptoms: Cervical or carotid bruit, Memory loss, Cluster type headache, Vertigo,
Aphasia/dysphasia, Previous stroke, Motor or sensory deficit, Syncope,
Fluctuating confusion, Amaurosis Fugax (transient monocular blindness),
Unilateral paralysis/weakness, Drop attacks, and Coronary or peripheral artery
disease.
 LOWER EXTREMITIES
ARTERIAL
LOWER EXTREMITIES
ARTERIAL
 LOWER
EXTREMITIES VENOUS
LOWER
EXTREMITIES VENOUS
 UPPER
EXTREMITIES ARTERIAL
UPPER
EXTREMITIES ARTERIAL
 UPPER
EXTREMITIES VENOUS
UPPER
EXTREMITIES VENOUS
LOWER EXTREMITIES
ARTERIAL – This exam uses sound
waves to obtain images and evaluate the arterial blood flow from the pelvis to
the foot. The images and Doppler waveforms are analyzed by a Cardiologist to determine
the location and extent of blockages. This exam takes approximately 45
minutes per leg. No preparation is needed. We highly recommend both legs be
scanned for comparative results.
Arterial
Symptoms: Claudication, Leg pain, Rest pain, Bruits, Gangrene, Diabetic neuropathy, Skin
color changes or ulceration, Absent or diminished distal or pedal pulses,
Distal extremity hair loss, Skin or nail infections, Hypertension, and Extreme
weakness or fatigue.
LOWER EXTREMITIES VENOUS – This exam uses sound waves to visualize the veins from the pelvis to the
foot. Doppler is used to evaluate blood flow in the veins. The physician views
these images to determine the presence of a blood clot or venous abnormality. This
exam takes approximately 45 minutes per leg. There is no preparation for
this exam. Please specify which leg or both.
Venous Symptoms: Edema,
Pitting edema, Pain, Increased limb tenderness, Anti-coagulant therapy
evaluation, Skin discoloration, Ulcers, Varicose veins and Pulmonary embolism.
UPPER EXTREMITIES VENOUS
or ARTERIAL – These exams use sound
waves and Doppler to evaluate the veins or arteries in the arm. Your own
physician will indicate which is needed. The Upper Extremity Venous will
visualize the presence of a blood clot. The Upper Extremity Arterial is done to
determine the severity of an arterial blockage. This testing takes less than
one hour. No preparation is needed. Please specify which arm or both.
Venous Symptoms: Edema,
Pain- tenderness, ulcers
Arterial Symptoms: Arm pain, skin or
nail infections, Skin color changes or ulceration, absent or diminished pulses,
gangrene, numbness and Positive Allen's test.
 COMPLETE
ABDOMEN
COMPLETE
ABDOMEN
 GALLBLADDER
GALLBLADDER
 KIDNEYS
(BLADDER AND RENAL)
KIDNEYS
(BLADDER AND RENAL)
 PANCREAS
PANCREAS
 LIVER/SPLEEN
LIVER/SPLEEN
 ABDOMINAL
AORTA
ABDOMINAL
AORTA
COMPLETE
ABDOMINAL – This exam is done to
image the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas and spleen. The test takes less than one hour.
Prior to this exam, nothing should be eaten or
drank for 8 hours. Medication
may be taken.
GALLBLADDER / LIVER– This exam is done to image the liver,
gallbladder, intra & extra hepatic biliary ductal system. The test takes less than 30 minutes.
Prior to this exam, nothing should be eaten or drank for 8 hours. Medication
may be taken.
Symptoms: Right or left
upper quadrant or flank pain, Abnormal lab values, Abdominal mass, Suspected
gallstones or bile duct stones, Jaundice, Suspected pancreatic disease,
Ascities, Unexplained weight loss, Cirrhosis, Nausea/vomiting, and Portal
hypertension.
RENAL / BLADDER / ABDOMINAL AORTA – This examines kidneys, renal and abdominal vessels, lymph
nodes and especially the abdominal aorta. Measurements are taken in various
planes. The test takes less
than one hour. Prior to this, there should be nothing eaten or
drank for 8 hours. Medication may be taken.
Symptoms: Hematuria, Flank or lower back pain,
Urinary tract infection, Abnormal lab values, Dysuria, Signs of renal failure,
mass, and Suspected abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 PELVIC
PELVIC
 THYROID
THYROID
PELVIC ULTRASOUND – This exam is done to
image the uterus, ovaries, vagina, urinary bladder and the surrounding region.
Measurements are taken. The test takes 30 minutes. A full bladder is
important; this helps push the bowel to the side so the pelvic organs are more
easily seen. One hour before the test, drink 4-6 large glasses of water.
Symptoms: Pelvic or abdominal pain, Pelvic
inflammatory disease, Palpable mass, Irregular menstrual cycle,
Infertility,
Endometriosis, Polycystic ovarian disease, Ovarian cysts, Vaginal bleeding or
discharges, Hematoma, Ascites and Unexplained weight loss.
THYROID ULTRASOUND– Imaging and measurements are taken in
various planes of the right and left lobes of the thyroid. The test takes 30
minutes. No preparation is needed.
Symptoms: Abnormal thyroid function,
Mass, and Hypercalcemia
|